The state-of-art milling plants of Rainbow Grains Pvt Ltd use 21st century technology. The online inflow and outflow mechanisms are fully computerized with the help of sensors. The plant has a production capacity exceeding 5 tons per hour, and is equipped with the latest milling machinery including pre cleaners, de-stoners, precision-sizers, graders, paddy separators, de-huskers, colour sorters etc. The plant premises are environment friendly and fully protected against contamination by foreign particles. A series of colour sorters and multi sorters are installed to ensure it is free from glass pieces, plastic granules, foreign material, dust, damaged, discoloured and unwanted grains.
RICE KERNEL COMPOSITION
A typical rice kernel of most rice varieties comprises of roughly
20% rice hull or husk, 11% bran layers, and 69% starchy
endosperm that is the milled rice as we know it.
In an ideal milling process, raw paddy will be processed
in the following fractions: 20% husk, 8−12% bran depending
on the milling degree and 68−72% milled rice -brown or white
rice depending on the variety. Total milled rice contains whole
grains or head rice, and brokens. The byproducts in rice milling
are rice hull, rice germ and bran layers, and fine brokens.
MILLING PROCESS
Milling is a crucial step in post-production of rice paddy. The
basic objective of a rice milling system is to remove the husk
and the bran layers, and produce an edible, white rice kernel
that is sufficiently milled and free of impurities.
Depending on the requirements of the customer, the rice should
have a minimum number of broken kernels. A rice milling system
can be a simple one or two step process, or a multi stage
process.
Commercial milling system uses multi stage milling process for
producing rice. The rice paddy undergoes a number of different
production steps to be ready for consumption:
- Pre-cleaning
- Parboiling
- De-Husking
- Paddy separation
- Whitening or polishing
- Mist polishing
- Grading and Separation of white rice
- Colour sorting
- Weighing & Packaging
PRE CLEANING
Paddy cleaning is done by paddy pre – cleaning machines. They ensure the removal of sand , mud , stone or any other form of dust particles from the paddy. The four stage process of soaking , cooking , drying and then milling follows the cleaning process.
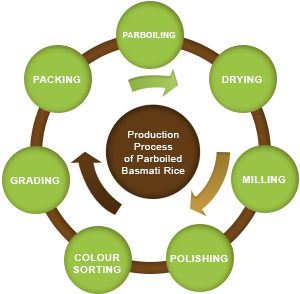
PARBOILING
This multi stage process involves the partial cooking of rice
paddy and involves the process of soaking, gelatinizing and
drying of paddy prior to milling. The objective is to impart a
required hardness on the grain (with husk intact) in order to
withstand milling operations. Rice is parboiled with the hull
intact, which softens the kernel, allowing the surface starch,
bran and other components to commingle thereby passing the
nutrients in the bran layer to the rice kernel. The water is
than drained and the rice is carefully steam dried. The dried
parboiled rice is sent through machines, which remove the hull
and polish the kernel.
Parboiling Process: Raw paddy intake from cleaning section is transferred to a paddy storage bin and then raw paddy steaming process takes place for 2 to 4 minutes. After this, paddy moved into soaking tanks. While in the paddy form, the rice soaked in water at ambient temperature (20-30 C) will take 36 to 48 hours to reach 30 -35 per cent moisture level but in hot water (60-65 C), this process takes much less time. Water temperature and length of soaking time affect the solubility of substances in rice as well as colour, smell, and taste. During hot water soaking (60-65 C), the grain absorbs moisture faster and reaches a moisture level of 30-35 per cent in 2 to 4 hours depending on the variety. Hot soaking keeps the grain at a higher temperature, which also reduces the steaming time needed during the next step to complete the parboiling process. The moisture content of paddy increases to about 38 per cent during steaming. Heating has a considerable effect on colour. When the steaming temperature exceeds 100 C, the colour becomes considerably deeper and the grain becomes harder. Longer steaming times also cause rice to be harder and darker. The process also may change depends on paddy as well as required output.
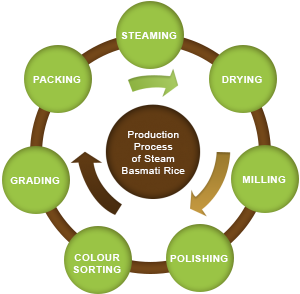
DRYING
Drying of par boiled paddy brings down the moisture content to 12 to 14 percent for safe storage and milling. The drying process is done in vertical chambers called dryers after which the paddy is ready for milling.
DEHUSKING
The dry paddy is passed into paddy separators to remove impurities and then into the milling machines which remove the husk thereby producing brown rice which is stored in a storage bin.
WHITENING
The brown rice is passed into whiteners and bran layer is removed and white rice kernels are extracted. The bran is rich in oil content and is sold as a byproduct.
MIST POLISHING
These machines use water at high pressure to give the white rice kernel a silky smooth finish.
COLOUR SORTING
Colour sorters are used to identify and remove not only impurities and foreign matter but also damaged or discoloured kernels. The finished white rice is then ready for grading.
GRADING
The graders use different sieves to separate rice according to the length of the grain and separate the broken kernels from the head rice.
PACKAGING
The finished rice is then weighed and packed in the desired packaging size and is ready to be shipped.